How websites impact the environment
Every time we surf the web, we are uploading, transferring and downloading data. These processes need electricity, and to generate this electricity we produce CO2. The servers hosting your website need electricity too. More people have access to the internet, and data gets faster and cheaper by the day, allowing us to consume more and faster, so the internet’s carbon emissions are growing too. The average website produces 1.76g of CO2 per page view according to Website Carbon. That equals to 2,112kg of CO2 emitted every year by each website with 100,000 monthly page views. However, according to the HTTPArchive, the average page loads in 1.9 seconds on desktop and 3.6 seconds on mobile. This means that we now have faster data transfer, but still slow page-load times. This is one way web design impacts the environment. We need to push web sustainability as a default of web development. Digital sector and the web in particular can help other sectors to reduce their carbon footprint, but we must account for our own digital emission. However, the risk is that the benefits do not outweigh the risks, so the first fundamental step is to measure a website’s carbon emissions. How websites create carbon emissions:- High-resolution images, videos, and complex animations increase the page weight and data transfer, leading to higher emissions. The more data that needs to be transferred to load a website, the more energy is required and the higher the carbon emissions.
- Complex websites features and dynamic content require more energy to load and process, resulting in greater carbon emissions (and therefore greater climate impact).
- Your web hosting and the energy sources powering the servers and data centers can significantly impact a website’s carbon footprint. Websites hosted on servers powered by non-renewable energy sources have a higher carbon impact
- Inefficient content management practices, such as using non-optimized images and fonts, can increase a website’s carbon emissions
- More page views and user activity lead to higher energy consumption and CO2 output
💡A content audit can help locate unnecessary elements that contribute to your website’s emissions.
Website owners and developers must take these factors into consideration in order to take practical steps to measure, benchmark, and reduce the carbon footprint of their websites. Unfortunately, there are so many more factors at play, that calculating the exact CO2 emissions of a website is not easy at all.
How to check your website carbon footprint
Years ago we developed a free tool for that (sitigreen.it), meant to spread awareness of digital sustainability in Italy by helping measure webpage carbon footprint. This tool is based on the Sustainable Web Design Model, an open-source/open-data model.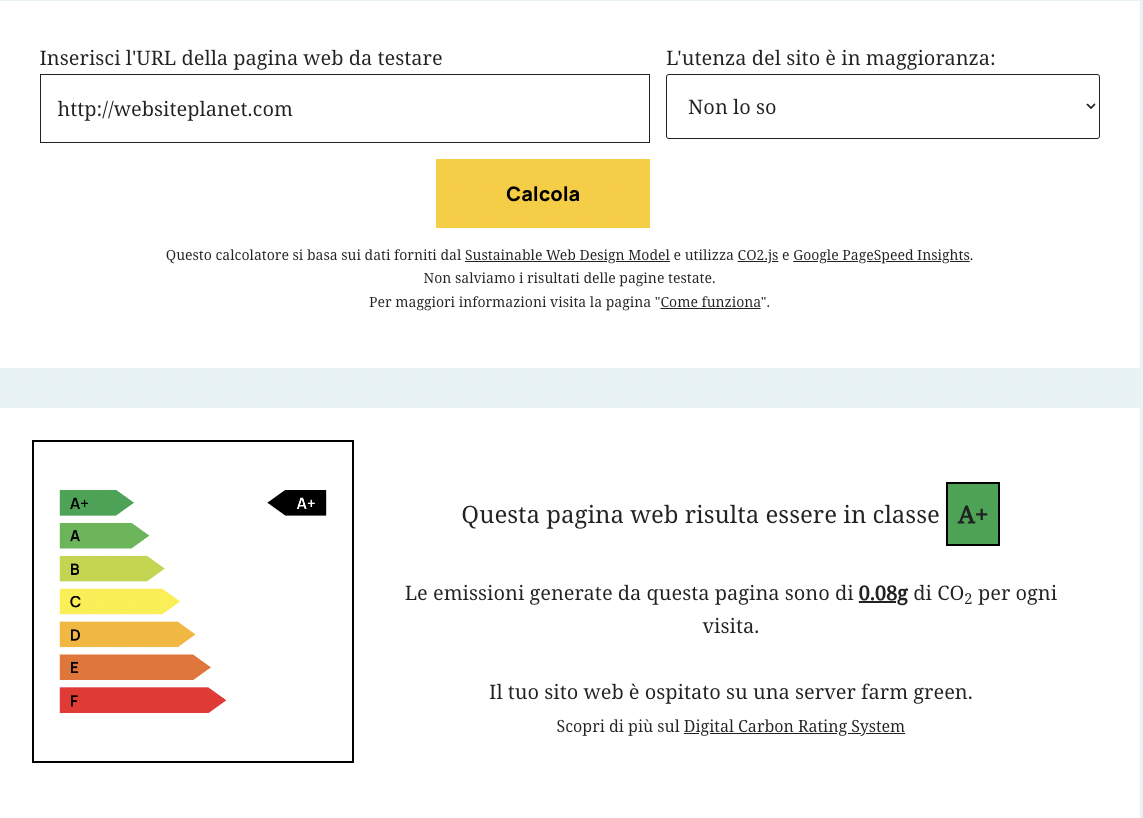
The best ways to reduce a website’s carbon footprint without increasing costs
The key is to focus on optimizing performance, choosing renewable energy sources, and adopting sustainable web development practices.Optimize website performance and content
Reduce page weight and data transfer by optimizing images, videos, and other media. Limit the number of images on each web page, and use formats like SVG and GIF instead of JPEG or PNG. An image compression tool will help you further reduce your images’ size. Avoid custom fonts as well. Caching and other performance optimization techniques also help reduce server processing.Choose a web host powered by renewable energy
Select a web hosting provider that uses renewable energy sources to power their data centers.Apply energy-efficient web development practices:
Adopt coding best practices that minimize energy consumption, such as efficient database management and use of caching, and the use of open-source tools and frameworks that prioritize sustainability, like the Sustainable Web Manifesto.Educate and engage the community
Most website owners are completely unaware of how their website’s impact on the environment. We all must raise awareness among fellow website owners, designers, and developers about the importance of web sustainability, collaboration and sharing of best practices.Websites sustainability myths debunking
Eco-friendly web design DOES NOT necessarily compromise on aesthetics
In fact, a well-designed website can be both visually appealing and highly accessible. The key is finding the right balance between aesthetics and accessibility. Look at Fantin’s website. The minimalist design prioritizes content over flashy graphics, and all the images are optimized through minimizing HTTP requests to deliver a flawless user experience while reducing the website’s carbon footprint.
Eco sustainable websites are cheaper in the long run
Sustainability in web design brings some interesting side effects. Developing a web page that saves resources may take more time, but it will be lighter and faster to load. Multiply this for all the pages on your website, and the difference becomes significant.
💡Less energy consumption improves performance
↪ Better performance gives a better UX
↪ Better UX Improves SEO Rankings
↪ Improved SEO rankings lower energy costs
↪ Lower Energy Costs = Money saved in the long run
Bonus: big ecommerce websites or web development agencies can save money every month on server costs.
At Piano D, Sustainable Web Design practices and Corporate Digital Responsibility principles are the factors we implement to solve this issue. We can reduce page weight and consequently their carbon footprint event up to 90%.
Websites’ page weight is always higher
Our goal is to invert this trend
The impact of AI
TL;DR The benefits of this new technology do not outweigh the risks. AI companies are consuming not only a lot of energy but also great amounts of groundwater to supply the cooling systems in their data centers. These cooling systems release harmful pollutants into the air and water, contributing to issues like smog, acid rain, and water/soil contamination.🚰 One input to ChatGPT consumes approximatelty one cup of fresh water
Even worse, many AI data centers have been built in developing countries with limited water resources and regulations, exacerbating the struggle to meet the needs for clean water in their fast-growing populations.
“Typically, companies care more about performance and cost; they do not take water intensity into account… We need to ensure that the environmental costs are fairly distributed across different regions for environmentally equitable AI, which is a crucial consideration for responsible AI.”Now the AI hype is at its peak, but I haven’t seen any life-changing application so far. We definitely need regulations to avoid a monopoly from a few providers, and we must build more awareness about the environmental impact and ethics of this technology. We’ve just been playing with it until now. Regardless of that, be aware of the environmental impact of digital technologies! Adopt greener digital behaviors and practice more conscious choices with your hardware and software suppliers.
Mohammad Atiqul Islam, assistant professor in computer science and engineering at the University of Texas in Arlington
📘Start making your website eco sustainable and accessible, by following the official WSG and WCAG guidelines:
- Web Sustainability Guidelines (WSG) 1.0:
https://w3c.github.io/sustyweb/ - Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1:
https://w3c.github.io/sustyweb/














